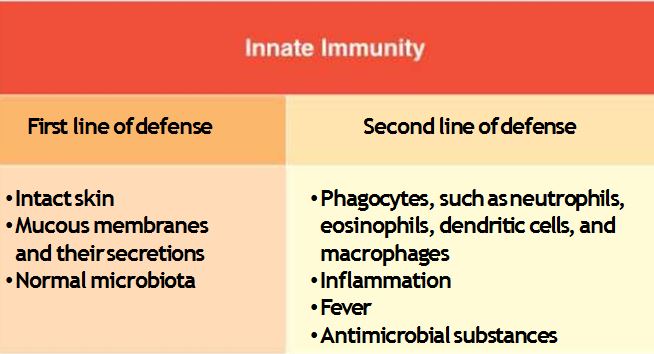
Physical Barriers: First Line of Defense
Skin
–Epidermis ;Outer layer – thin
Layers of tightly packed epithelial cells
Outermost layers dead –Keratin (Protein)
–Sloughs off routinely
–Dermis; Inner layer(thick)
Connective tissue
Bacteria enter through Skin ONLY when skin is damaged.

Mucous Membranes
- Line respiratory, gastrointestinal, urogenital
- Epithelial cells with inner connective tissue
Goblet cells; Secrete mucus (glycoproteins)
Prevents dessication, traps microbes, enzymes to kill microbes
-Mucus-coated nose hairs: Trap microbes
- Ciliary escalator
Ciliated cells of Lower Respiratory Tract
Mucus-coated dust/microbes pushed outward
Sneezing/ Coughing speed up process
- Epiglottis; Covering over larynx: prevents food and microbes getting in
Other Physical/Chemical Barriers
- Tears; Lacrymal Glands: Under upper eyelid
Constantly wash over eye; drain into lacrymal ducts
Lysozyme (breaks peptidoglycan walls of bacterial cell walls)
•Urine; Flushing mechanism prevents colonization
Contains uric acid, urea (makes pH ~6.5), lysozyme
•Saliva ;Salivary Glands
Constantly washes over teeth and mouth
Contains Lysozyme
•Peristalsis ;Movement of food by coordinated contractions
Defecation
Vomiting in response to microbial toxins
'Reference > Immunology' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Nk cell (0) | 2019.07.02 |
|---|---|
| NK 세포 (0) | 2019.07.02 |
| 항원과 항체 작용 (0) | 2019.06.26 |
| 면역글로불린(immunoglobulin)의 종류와 기능 (0) | 2019.06.26 |
| 항원과 항체 (0) | 2019.06.26 |



