
Southern blot : DNA detection
Northern blot : RNA detection
Western blot : Protein detection
Western blot
Western blot은 찾고자 하는 protein의 antigen epitope과 반응하는 antibody를 이용하여 단백질 혼합 물 중에서 원하는 단백질(antigen)만을 찾아내는 방법이다.
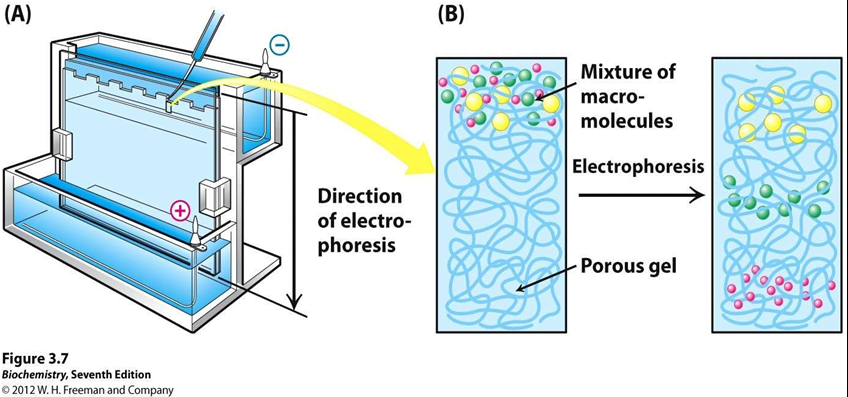
전기영동을 이용하여 단백질을 gel 상에서 크기에 따라 분리한 후, PVDF, nylon과 같은 membrane에 transfer한다. Membrane에 발광하는 probe가 붙어있는 antibody(항체)를 이용하여 찾고자 하는 특정 단백질을 검출한다.
여러가지 단백질 중에서 원하는 단백질만을 보는 방법으로 fluorescence (fluorescein isothiocyanate), radioactivity, enzyme reaction (peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase, glucose oxidase) 등의 방법이 이용되고 있다.
Western blot workflow
SAMPLE PREPARATION
• DETERGENT LYSIS FOR TISSUE CULTURE
• ULTRASONICATION FOR CELL SUSPENSION
• MECHANICAL HOMOGENIZATION FOR PLANT AND ANIMAL TISSUES
• ENZYMATIC DIGESTION FOR BACTERIAL, YEAST AND FUNGAL CELLS
GEL ELECTROPHORESING THE PROTEIN SAMPLE
• Electrophoresis is commonly used method for separating proteins on the basis of size, shape or charge.
• In Gel electrophoresis, protein of sample extract are separated according to their molecular weight.
PROTIEN TRANSFER
• On completion of the separation of proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, the next step is to transfer the proteins from the gels to solid support membrane.
• Usually made up of a chemically inert substance, such as NITROCELLULOSE or PVDF.
• The process of transferring proteins from a gel to a membrane while maintaining their relative positions and resolutions is known as BLOTTING
PROTIEN STAINING
• After gel electrophoresis, it may be necessary to confirm that all the proteins in the gel have been completely eluted.
• As proteins are not directly visible in the gel, the gel must be stained.
• Proteins are usually stained with dyes such as coomassie blue, silver stain, or deep purple.
• After staining, a permanent record may be made by imaging the gel with suitable instrument.
BLOCKING NON-SPECIFIC ANTIBODY
• For meaningful results, the antibodies must bind only to the protein of interest and not to the membrane.
• Non-specific binding (NSB) of antibodies can be reduced by blocking the unoccupied sites of membrane with an inert protein or non-ionic detergent.
• Blocking agents should possess greater affinity towards membrane than the antibodies.
• The most common blocking agents are:
- Bovine serum albumin(BSA)
- Non-fat milk
- Casein
- Gelatin
- Dilute solution of Tween 20.
ANTIBODY PROBING
• After blocking , the blot is incubated with one or more antibodies.
• This uses specific antibody to detect a localize the protein blotted to a membrane.
• The specificity of antigen-antibody binding permits the identification of a single protein in a complex sample
• The non-labeled primary antibody directed against the target protein, and specific labeled secondary antibody binds to the primary antibody.
• The secondary antibody is conjugated to an enzyme that is used to indicate the location of the protein
• Secondary antibodies can be a monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies.
•The secondary antibodies not only serves as a carrier of the label, but it is also helps to amplify the emitted signals.
• The signal emitted by the labeled secondary antibody is then measured and is proportional to the quantity of protein of interest present on the membrane.

WASHING
• Unbound antibodies can cause high background and poor detection.
• Hence Washing the blot removes unbound antibodies from the membrane.
• A dilute solution of tween-20 in TBS or PBS buffer is commonly used for washing.
PROTIEN DETECTION
• After the unbound probes are washed away, the western blotting is now ready for detection of the probes that are labeled and bound to the protein of interest.
• Enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase(AP), & Horse-radish peroxidase(HRP) are widely used in detection of proteins.
• There are four methods of detection can be done & they are as follows:
DIGITAL IMAGING
• This is the last & major step of the western blotting technique.
• Detection of signals, using either X-Ray film, scanners or a CCD, results in one or more visible protein bands on the membrane image.
• The molecular weight of the protein can be estimated by comparison with marker proteins and the amount of protein can be determined as this is related to band intensity.
• Qualitative & quantitative analysis can be done in order to verify the absence or presence of specific proteins of interest